Use Secret Manager to handle sensitive data in Firebase Cloud Functions 573 words.
Last Updated
Secret Manager is a new service on Google Cloud that allows us to store and version sensitive data like private API keys and passwords, then access it from any cloud service. It provides encryption, audit logging, versioning, and IAM roles for secure fine-grained control over sensitive information.
A common use-case for a Firebase apps is the management of secret API keys in a Cloud Function. The following lesson will teach you how add secrets via the Google Cloud console, then read them from a Firebase Cloud Function with Node.js.
Secret Manager OR Functions Environment Variable?
Should you use Secret Manager OR a Cloud Functions Environment Variable? It is possible to set environment variables in Firebase by running a command like this:
firebase functions:config:set someservice.key="mysecret"
This works great most of the time, but has a few drawbacks…
- requires all cloud functions to re-deploy when changed
- can’t be shared with other services
- can’t be versioned
Secret Manager solves all of these problems, BUT is also has some drawbacks of it’s own:
- more work to setup initially
- secrets retrieved asynchronously, so my incur a performance penalty
Those are the tradeoffs. Cloud Functions env vars are great for most situations, but Secret Manager is nice when dealing the dynamic secrets shared across multiple Google services.
Create a Secret
Enable the Secret Manager API
First, enable the Secret Manager API for your project from the Google Cloud console.
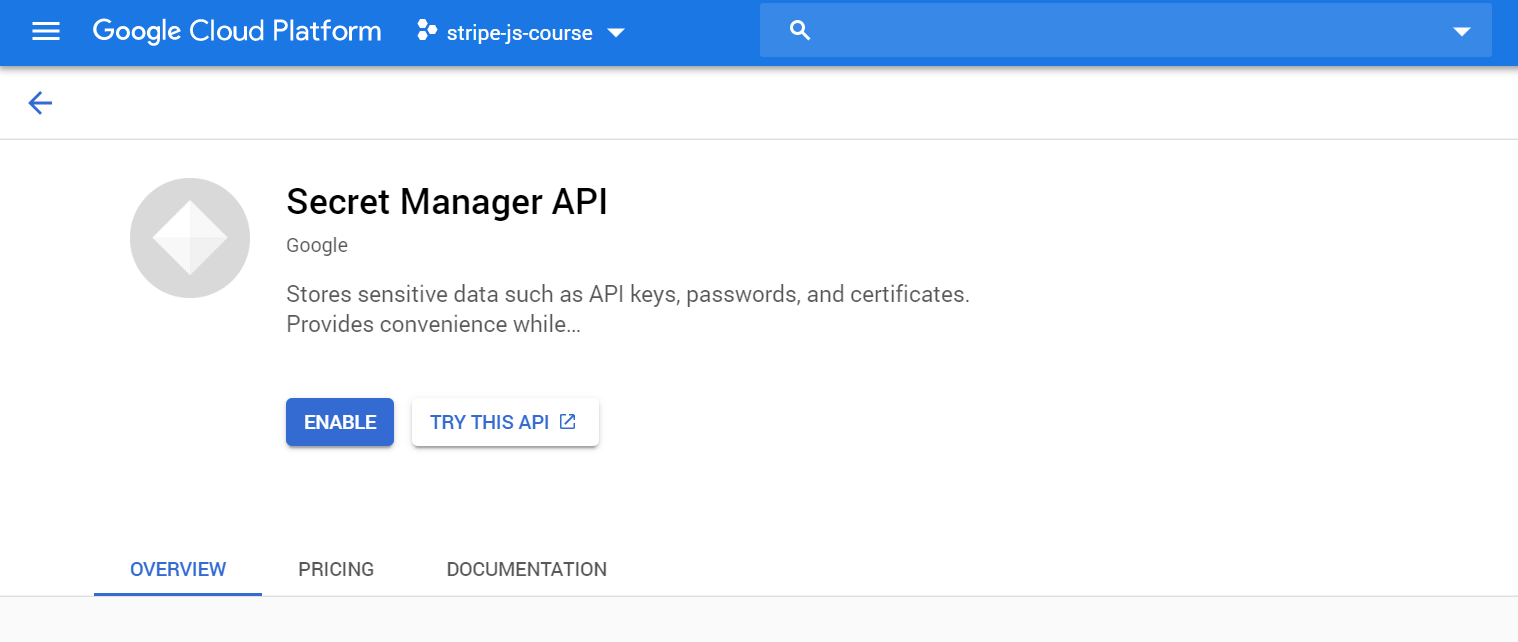
Enable the Secret Manager API
Add a Secret from the Console
From the GCP console, navigate to Security » Secret Manager. Add a new secret and make note of its name.
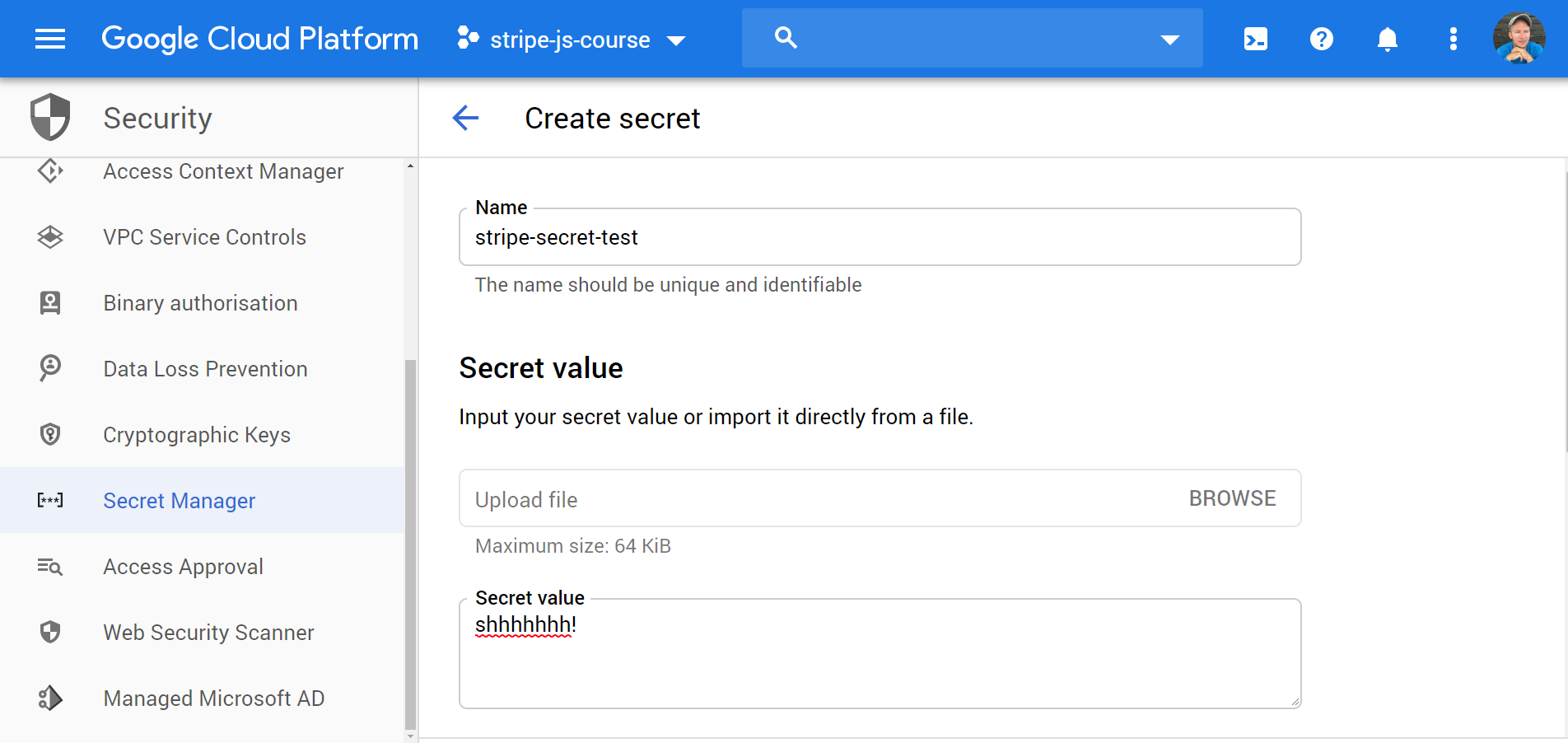
Create a secret from the console
Grant Cloud Functions the required IAM role
By default, only the primary Google Cloud admin account can read/write secrets. In order to give the Cloud Functions runtime access, find the App Engine default service account member in the IAM tab and edit its roles to include the secretmanager.secretAccessor role.
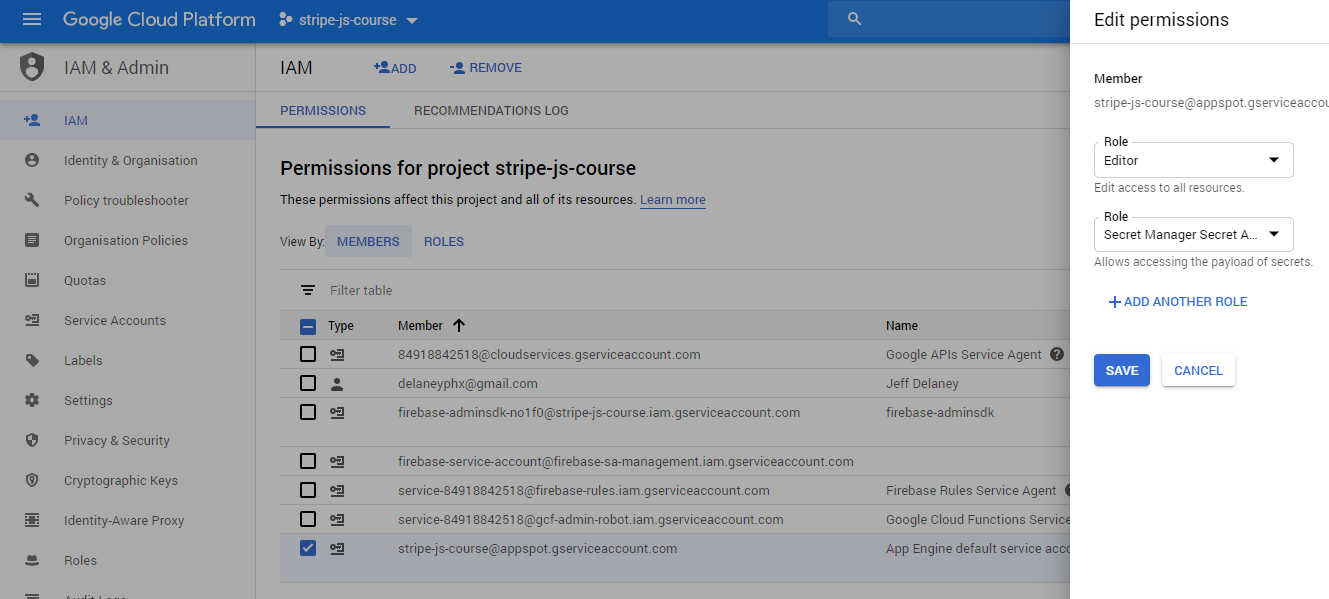
Add Secret Accessor role to the App Engine default service account
Read Secrets in Cloud Functions
Perform the following steps from your Cloud Functions environment. This example uses Node.js and TypeScript.
Installation
npm install @google-cloud/secret-manager
This package requires Node 10. Update the engine value to enable the Node 10 runtime.
"engines": {
"node": "10"
},
If using TypeScript, update your tsconfig with the following values:
{
"compilerOptions": {
// ...omitted
"lib": ["ESNext"],
"strictNullChecks": false
},
}
Instantiate the Secret Manager client in your code to read and manage secrets. Currently, it can only READ our secret values because of the IAM role assigned in the previous section. Upgrade the IAM role if you also want your functions to modify secrets.
import * as functions from 'firebase-functions';
import { SecretManagerServiceClient } from '@google-cloud/secret-manager';
const secrets = new SecretManagerServiceClient();
Read Secret Values
Create a helper function to read your secret as a string. The payload also contains additional metadata about the secret. It expects the full path to the secret value, along with the version - use the keyword latest to grab the most recent version.
async function getSecretValue(name: string) {
const [version] = await secrets.accessSecretVersion({
name: `projects/stripe-js-course/secrets/${name}/versions/latest`,
});
const payload = version.payload?.data?.toString();
return payload;
}
You can now use this value in your Cloud Functions.
export const helloWorld = functions.https.onRequest(
async (request, response) => {
const mySecret = await getSecretValue('hello-world');
// Warning: not a good idea to console log secrets in production
console.log(mySecret)
}
);
Secret Manager is a new service on Google Cloud that allows us to store and version sensitive data like private API keys and passwords, then access it from any cloud service. It provides encryption, audit logging, versioning, and IAM roles for secure fine-grained control over sensitive information.
A common use-case for a Firebase apps is the management of secret API keys in a Cloud Function. The following lesson will teach you how add secrets via the Google Cloud console, then read them from a Firebase Cloud Function with Node.js.
Secret Manager OR Functions Environment Variable?
Should you use Secret Manager OR a Cloud Functions Environment Variable? It is possible to set environment variables in Firebase by running a command like this:
firebase functions:config:set …Upgrade to PRO for the Full Lesson
Monthly
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Cancel anytime
- Slack #pro-member invite
- AngularFirebase Survival Guide Book
- No ads
Quarterly
- All monthly tier benefits
- 💰 33.33% discount
- 🔥 Free Sticker
---- OR ----
You must be logged in to view this content.
