Build an Infinite Virtual Scroll with the Angular CDK 817 words.
Last Updated
The release of Angular v7 gives us access to a new virtual scroll behavior in the Material Component Development Kit (CDK). It provides tools for looping over a lists that only render elements when they are visible in the viewport, preventing lag an janky-ness in the browser. As an added bonus, it exposes a reliable API for building an infinite scroll where new batches of data are retrieved automatically when the user scrolls to the bottom of the list.
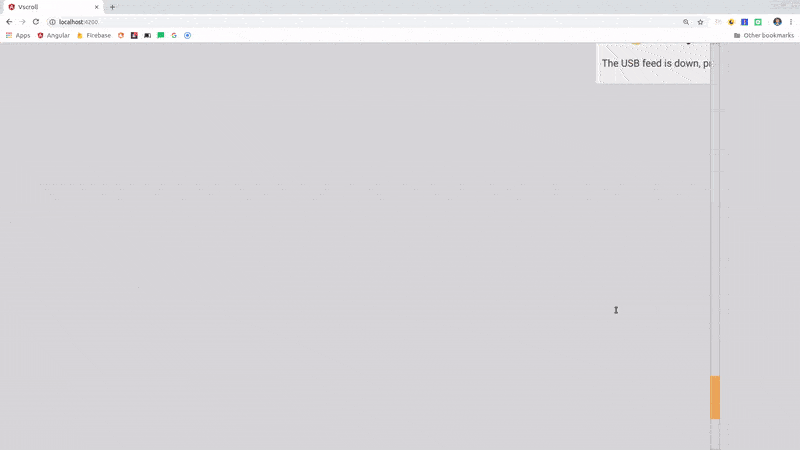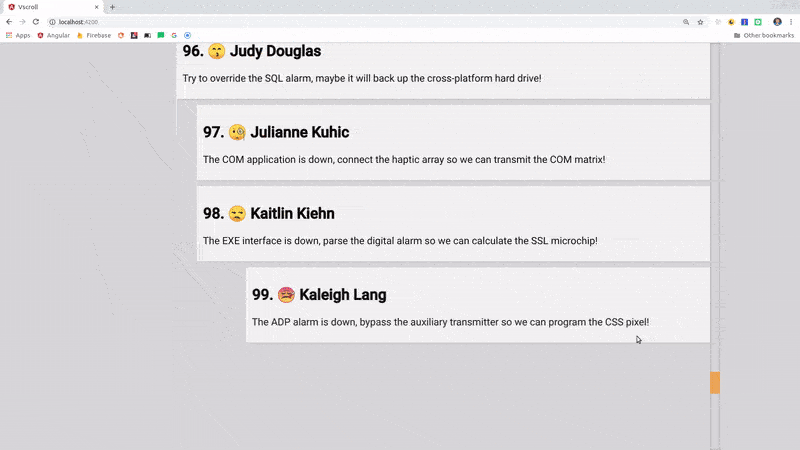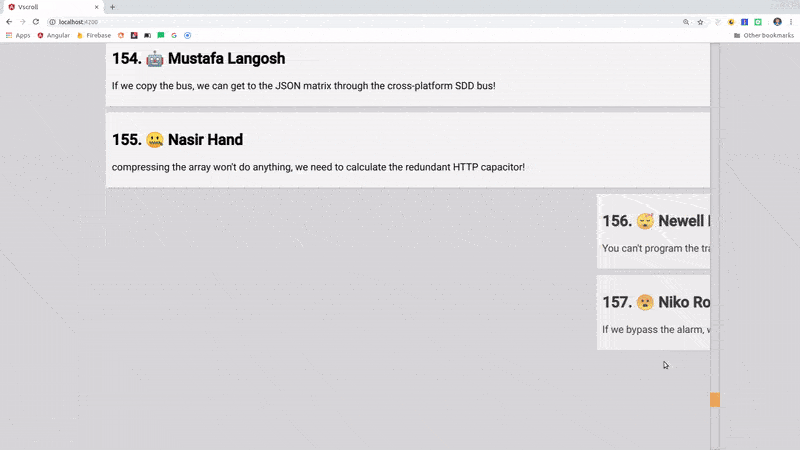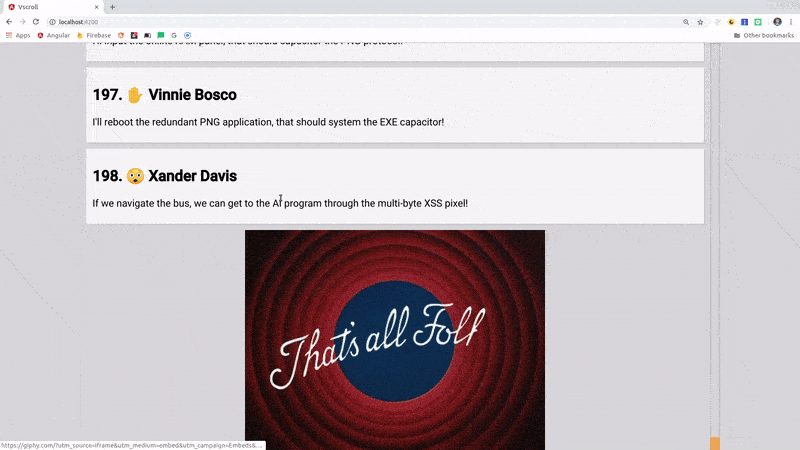
Angular CDK Virtual Scroll Demo
Installation
First, make sure you’re updated to Angular v7.0 or later, then add Angular Material to your project.
npm i @angular/cli@latest -g
ng new myApp
ng add @angular/material
Angular CDK Virtual Scroll Basics
Let’s start by reviewing a few important concepts with virtual scroll. First, you declare the cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport component to provide a context for virtual scrolling. It should have an itemSize input property defined as the pixel height of each item. The *cdkVirtualFor is a replacement for *ngFor that you can use to loop over a list.
<cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport itemSize="100">
<li *cdkVirtualFor="let person of people">
{{ person }}
</li>
</cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport>
CSS Requirements
The cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport must have a height and the items it loops over should also have a fixed height. The component needs this information to calculate when an item should be rendered or removed.
cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport {
height: 100vh;
li {
height: 100px;
}
// Bonus points
&::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 1em;
}
&::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
-webkit-box-shadow: inset 0 0 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
&::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
background-color: rgb(238, 169, 79);
}
}
Custom Events
The component emits a custom event whenever the scrolled index changes. This allows you to run code when a specific item is scrolled to.
<cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport itemSize="100" (scrolledIndexChange)="handler($event)">
</cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport>
Accessing the Component API
The CdkVirtualScrollComponent component class contains a suite of API methods that can be called to scroll programmatically or to measure the size of the viewport. You can gain access to these methods by grabbing the virtual scroll component with ViewChild.
import { Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { CdkVirtualScrollViewport } from '@angular/cdk/scrolling';
export class MyComponent {
@ViewChild(CdkVirtualScrollViewport)
viewport: CdkVirtualScrollViewport;
// example
go() {
this.viewport.scrollToIndex(23)
}
}
Building a Realtime Infinite Virtual Scroll
You will need @angular/fire and Firebase installed to follow along with the next section.
Building a realtime infinite scroll is a challenging requirement. We have tackled infinite scroll with Firestore in the past, but opted out of realtime listeners to simplify the code. Today, the CDK makes our life so much easier that we will make the extra effort to make our infinite list respond to realtime updates.
The code below gets fairly complex, so let’s look at the main instructions step-by-step.
- Make a paginated query to Firestore using
ref.orderBy(name).startAt(lastSeen).limit(batch). - Map the documents array to an object, where each key is the document ID (this mapping is needed for realtime updates).
- Scan the source observable and merge in new batches.
- Flatten the object values into a single array for looping in the HTML.
Keep in mind, this strategy works well for realtime data changes, but does not automatically reorder the list or remove deleted items. Additional clientside monkey patching will be needed to resolve these limitations.
Full Infinite Scroll Code
import { Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { CdkVirtualScrollViewport } from '@angular/cdk/scrolling';
import { AngularFirestore } from '@angular/fire/firestore';
import { Observable, BehaviorSubject } from 'rxjs';
import { map, tap, scan, mergeMap, throttleTime } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Component({
selector: 'app-infinite-scroll',
templateUrl: './infinite-scroll.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./infinite-scroll.component.scss']
})
export class InfiniteScrollComponent {
@ViewChild(CdkVirtualScrollViewport)
viewport: CdkVirtualScrollViewport;
batch = 20;
theEnd = false;
offset = new BehaviorSubject(null);
infinite: Observable<any[]>;
constructor(private db: AngularFirestore) {
const batchMap = this.offset.pipe(
throttleTime(500),
mergeMap(n => this.getBatch(n)),
scan((acc, batch) => {
return { ...acc, ...batch };
}, {})
);
this.infinite = batchMap.pipe(map(v => Object.values(v)));
}
getBatch(offset) {
console.log(offset);
return this.db
.collection('people', ref =>
ref
.orderBy('name')
.startAfter(offset)
.limit(this.batch)
)
.snapshotChanges()
.pipe(
tap(arr => (arr.length ? null : (this.theEnd = true))),
map(arr => {
return arr.reduce((acc, cur) => {
const id = cur.payload.doc.id;
const data = cur.payload.doc.data();
return { ...acc, [id]: data };
}, {});
})
);
}
nextBatch(e, offset) {
if (this.theEnd) {
return;
}
const end = this.viewport.getRenderedRange().end;
const total = this.viewport.getDataLength();
console.log(`${end}, '>=', ${total}`);
if (end === total) {
this.offset.next(offset);
}
}
trackByIdx(i) {
return i;
}
}
HTML
<ng-container *ngIf="infinite | async as people">
<cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport itemSize="100" (scrolledIndexChange)="nextBatch($event, (people[people.length - 1].name))">
<li *cdkVirtualFor="let p of people; let i = index; trackBy: trackByIdx" class="animated lightSpeedIn">
<h2>{{ i }}. {{ p.emoji }} {{ p.name }}</h2>
<p> {{ p.bio }} </p>
</li>
<iframe *ngIf="theEnd" src="https://giphy.com/embed/lD76yTC5zxZPG" width="480"
height="352" frameBorder="0" class="giphy-embed" allowFullScreen></iframe>
</cdk-virtual-scroll-viewport>
</ng-container>
The End
The CDK dramatically improves the handling of scroll-able lists in Angular. In this demo, we managed to convert a Firestore Collection into an animated, realtime, infinite, virtual list with less than 100 lines of code. That’s pretty amazing considering how complex a feature like this would be without the help of Angular + Firebase.
