A comprehensive guide to server-side rendering with Angular Universal and Firebase 1201 words.
Last Updated
Health Check
@angular/core@7.2
firebase-functions@2
node@8.14.0
Nothing beats the user experience of a single page JS app on the web, but you sacrifice the ability to share metatags with social media bots and search engines on deep links. Fortunately, you can overcome this limitation with server-side rendering (SSR) via Angular Universal.
The following lesson will show you how to setup Angular Universal with ExpressJS. In addition, you will learn how to deploy the app with (1) Node via AppEngine or (2) Firebase Cloud Functions - both of which are are on the free tier.
Step 0: Prerequisites
- Install Angular ✔️ How to install Angular
- Install @angular/fire ✔️ How to install @angular/fire, aka AngularFire2
- Install Google Cloud SDK
- Install Firebase Tools
Step 1: Setup Universal in Angular
NG Add Universal
ng add @nguniversal/express-engine --clientProject myappThis will add several new files to your project. The Angular Universal app is used to render your angular code on a server:
- src/main.server.ts
- src/app/app.server.module.ts
- src/tsconfig.server.json
Then ExpressJS is the actual server that will handle requests/responses and is defined by these files:
- webpack.server.config.js
- server.ts
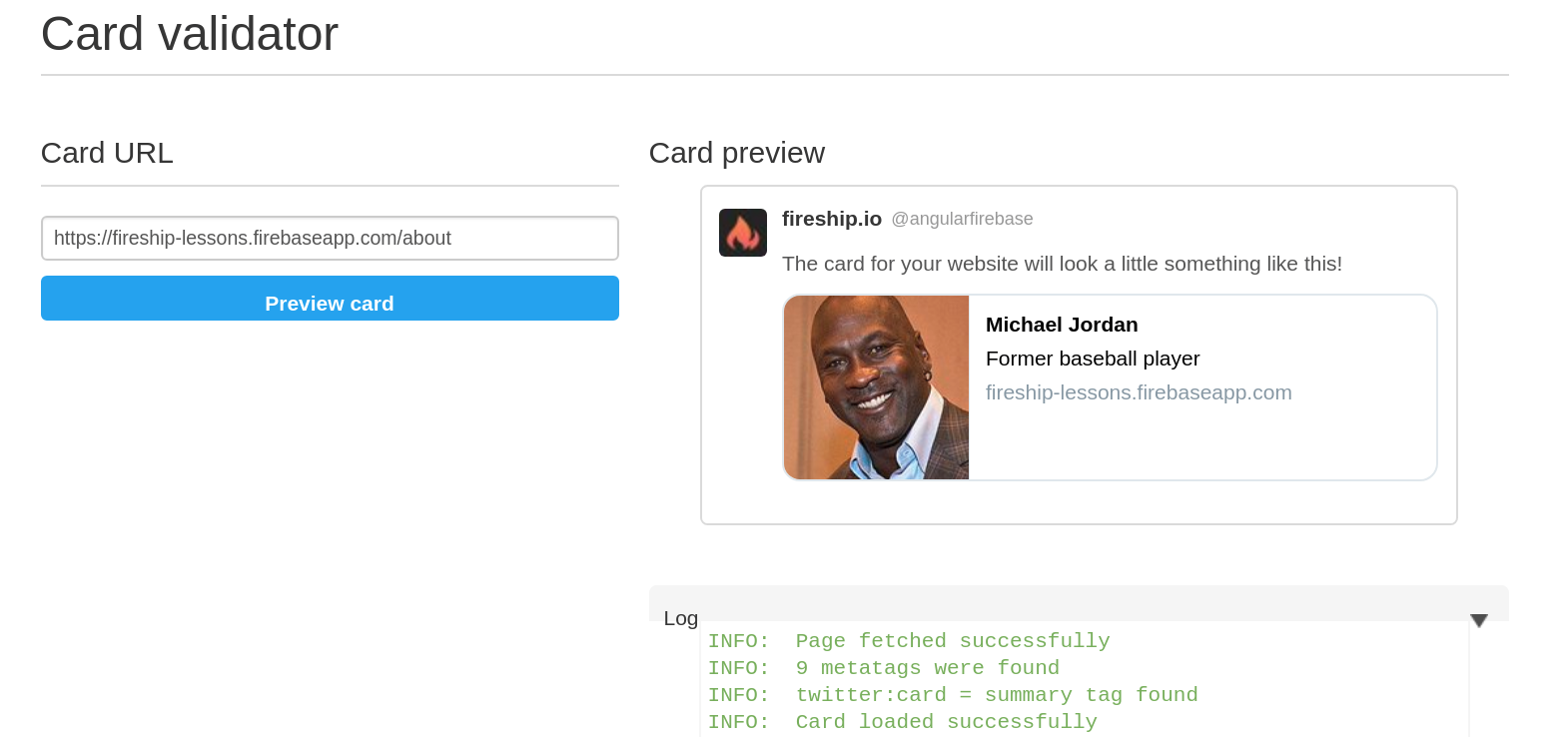
Step 2: Render Dynamic Titles and Meta Tags in Angular
Our angular app needs a router-loaded component that generates its own metatags. The following example will hard code the meta tags, but you can also build them dynamically by reading data from your database.
ng g component about -m appConfigure the Router
At this point, let’s build a basic component that renders dynamic meta tags based on the route ID.
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { AboutComponent } from './about/about.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent }
];
Create the Component
Angular has built-in services to change the title and metatags in the document body.
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Title, Meta } from '@angular/platform-browser';
@Component({
selector: 'app-about',
templateUrl: './about.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./about.component.scss']
})
export class AboutComponent implements OnInit {
data = {
name: 'Michael Jordan',
bio: 'Former baseball player',
image: 'avatar.png'
};
constructor(private title: Title, private meta: Meta) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.title.setTitle(this.data.name);
this.meta.addTags([
{ name: 'twitter:card', content: 'summary' },
{ name: 'og:url', content: '/about' },
{ name: 'og:title', content: this.data.name },
{ name: 'og:description', content: this.data.bio },
{ name: 'og:image', content: this.data.image }
]);
}
}
Step 3: Compile/Test the Server Locally
Compile the Server
Open the package.json file and you’ll notice four new scripts related to SSR. Run the commands below to compiple the TypeScript code and run the Express server on localhost:4000.
npm run build:ssr
npm run serve:ssrAt this point, you should see an error that looks like this because our server is thowing an error for missing XHLHttpRequest. See the next step to fix it.
Add Firebase Polyfills to Express
Firebase uses Websockets and XHR not included in Angular that we need to polyfill.
npm install ws xhr2 bufferutil utf-8-validate -DThen declare them on Node global at the top of the server file.
(global as any).WebSocket = require('ws');
(global as any).XMLHttpRequest = require('xhr2');
// ...
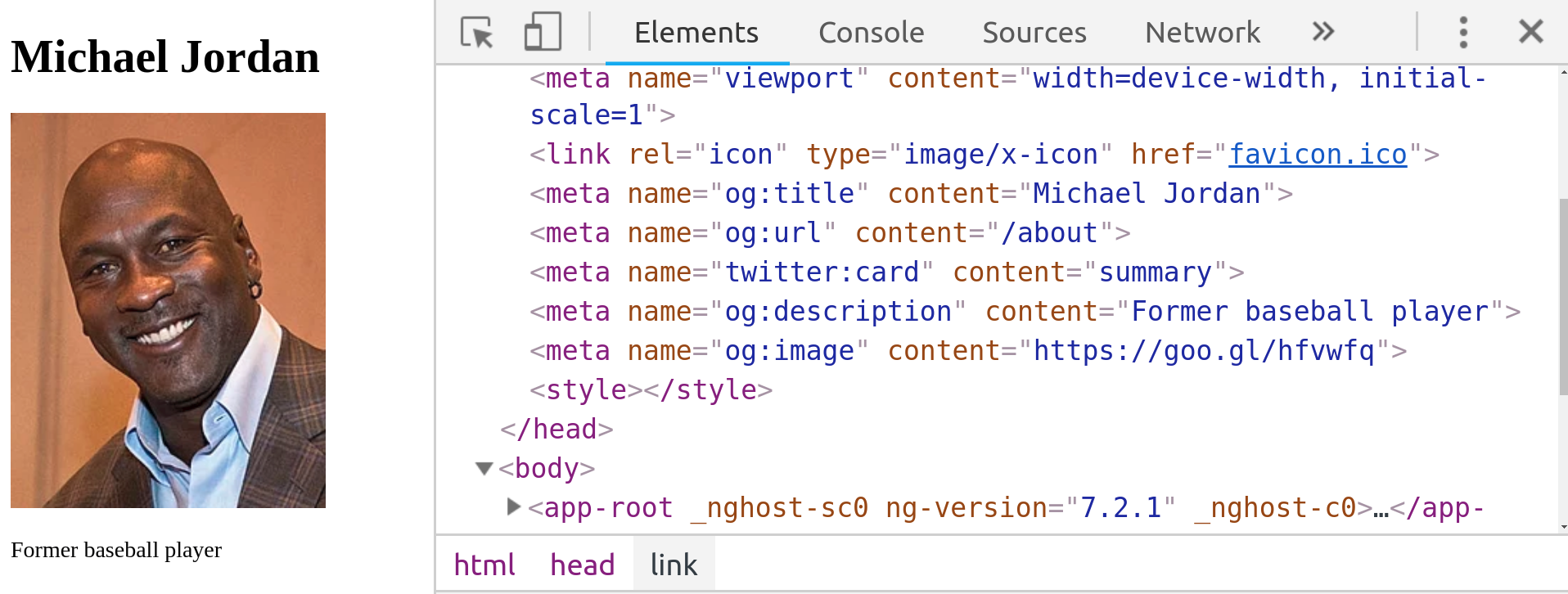
Rebuild your app and restart the server. The HTML returned from Express should now include custom meta tags.
Deploy Option A - AppEngine Node Standard
Command Line Deploy
Deploying to AppEngine will containerize your code allow it to scale infinitely in the cloud. It starts on a free tier and can scale up automatically based on traffic or resource demands.
Crate an app.yaml file in the root the project. The standard environment for Node8 and Node10 is free to deploy with a small instance and can automatically scale the moon 🌙 as needed.
runtime: nodejs8With Google Cloud SDK installed on your system, simply run the deploy command.
gcloud app deployAlso, update the start command in the package.json to run Express server.
{
"scripts": {
"start": "npm run serve:ssr"
}
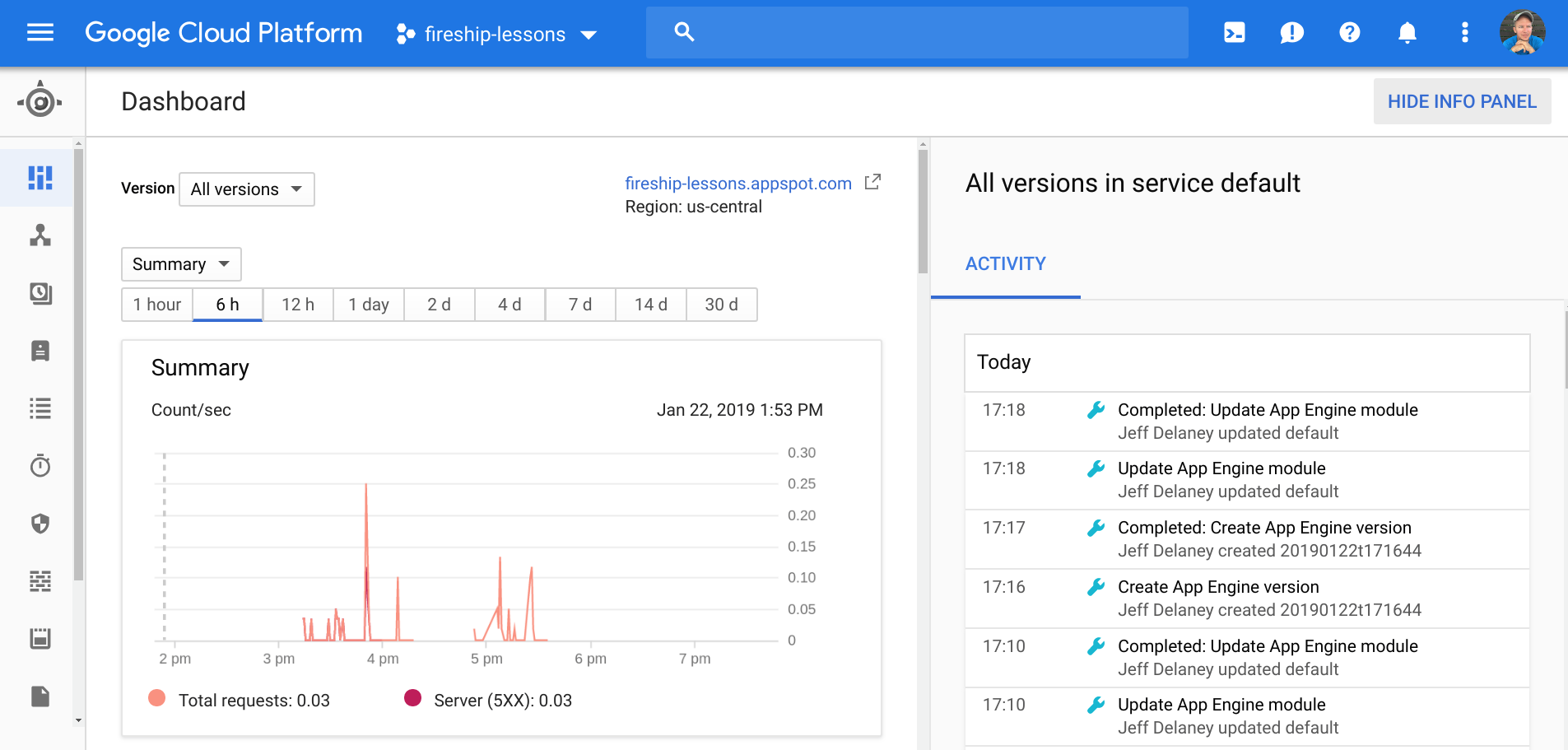
}If all went according to plan, you should now see your app on the AppEngine dashboard.
Deploy Option B - Firebase Cloud Functions
An alternative to AppEngine is to rewrite your Firebase Hosting rules to a Firebase Cloud Function.
firebase init
# select hosting, functionsNow make your public folder dist/browser, but rewrite all traffic to a function.
{
"hosting": {
"public": "dist/browser",
// ...
"rewrites": [
{
"source": "**",
"function": "ssr"
}
]
}
}Remove the Express Server Listener
When deploying to AppEngine we need to tell the server to listen to requests. In Cloud Functions, this is already happening under the hood, so we need to update our server code.
Make sure to export the express app, then remove the call to listen.
export const app = express();
// ...
// remove or comment out these lines 👇
// Start up the Node server
// app.listen(PORT, () => {
// console.log(`Node Express server listening on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
// })
//
Update the Webpack Config
We need to tell the Webpack to package our server code as a library that can be consumed by the Node function. Update the existing config with the following changes.
output: {
// Puts the output at the root of the dist folder
path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist'),
library: 'app',
libraryTarget: 'umd',
filename: '[name].js',
},
Make sure to rebuild the Angular app with npm run build:ssr.
Copy the Angular App to the Function Environment
The cloud function needs access to your Angular build in order to render it on the server. Let’s write a simple node script that copies the most recent Angular app to the functions dir on build.
cd functions
npm i fs-extra
const fs = require('fs-extra');
(async() => {
const src = '../dist';
const copy = './dist';
await fs.remove(copy);
await fs.copy(src, copy);
})();
Update the build script to copy over your Angular files. While here, you can also mark this function to be deployed with Node v8.
{
"name": "functions",
"engines": {
"node": "8"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "node cp-angular && tsc"
}
}The function itself only needs to import the universal app into the current working directory. That’s why we need to copy it to the function’s environment.
import * as functions from 'firebase-functions';
const universal = require(`${process.cwd()}/dist/server`).app;
export const ssr = functions.https.onRequest(universal);
You can test it by serving both the hosting and function simultaneously - the moment of truth…
cd functions
npm run build
firebase serveYou should now be able to visit your server rendered site on localhost:5000.
If it looks good, deploy the app with a single command:
firebase deploy