Learn the basics of React & Firebase by building a simple group chat app from scratch. 663 words.
Last Updated
The following tutorial demonstrates how to build a simple group chat app with React and Firebase. The goal of this lesson is to showcase important beginner concepts when working with the ⚛️🔥 React Firebase stack, including user authentication, firestore, and security rules.
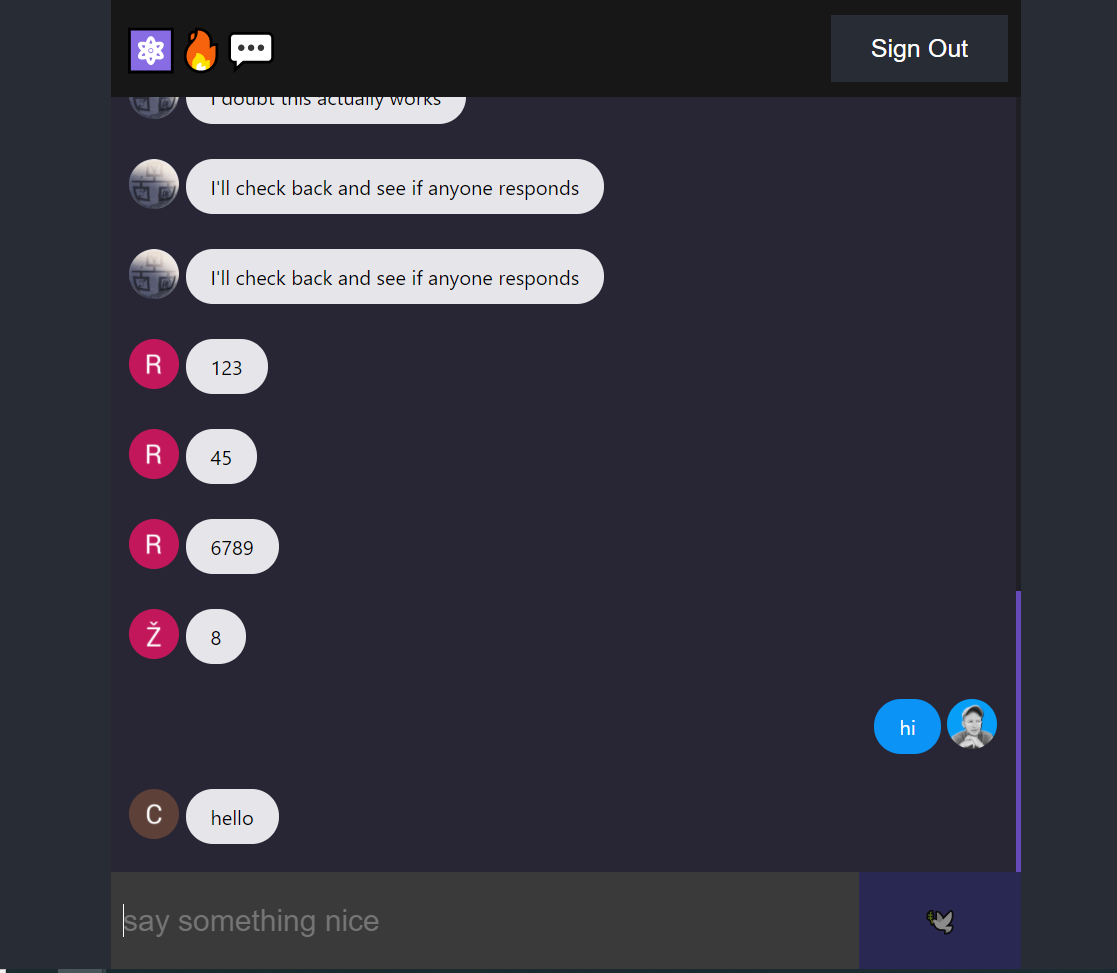
React Firebase Chat Demo
Important Links
Initial Setup
Firebase Project
Create a free Firebase project. Make sure to enable Google SignIn and and activate Cloud Firestore.
Create a React App
Create a react app and install the required dependencies.
npx create-react-app superchat
cd superchat
npm install react-firebase-hooks firebase
Initialize your Firebase project in React.
import React, { useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import firebase from 'firebase/app';
import 'firebase/firestore';
import 'firebase/auth';
import { useAuthState } from 'react-firebase-hooks/auth';
import { useCollectionData } from 'react-firebase-hooks/firestore';
firebase.initializeApp({
// your config
});
const auth = firebase.auth();
const firestore = firebase.firestore();
function App() {
const [user] = useAuthState(auth);
return (
<div className="App">
<header>
<h1>⚛️🔥💬</h1>
<SignOut />
</header>
<section>
{user ? <ChatRoom /> : <SignIn />}
</section>
</div>
);
}
function SignIn() {}
function SignOut() {}
function ChatRoom() {}
function ChatMessage() {}
User Authentication
The following components allow a user to Sign in with Google.
SignIn
function SignIn() {
const signInWithGoogle = () => {
const provider = new firebase.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
auth.signInWithPopup(provider);
}
return (
<button onClick={signInWithGoogle}>Sign in with Google</button>
)
}
SignOut
function SignOut() {
return auth.currentUser && (
<button onClick={() => auth.signOut()}>Sign Out</button>
)
}
Chat Room
Read Chat Messages
Make a query to the database, then listen to the data in realtime with the useCollectionData hook.
function ChatRoom() {
const messagesRef = firestore.collection('messages');
const query = messagesRef.orderBy('createdAt').limitToLast(25);
const [messages] = useCollectionData(query, { idField: 'id' });
return (<>
<main>
{messages && messages.map(msg => <ChatMessage key={msg.id} message={msg} />)}
</main>
</>)
}
function ChatMessage(props) {
const { text, uid, photoURL } = props.message;
const messageClass = uid === auth.currentUser.uid ? 'sent' : 'received';
return (<>
<div className={`message ${messageClass}`}>
<img src={photoURL} />
<p>{text}</p>
</div>
</>)
}
Create New Messages
Use a form to collect the user’s message, then submit it to firestore to perform a write to the database.
function ChatRoom() {
// ... omitted
const [formValue, setFormValue] = useState('');
const sendMessage = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const { uid, photoURL } = auth.currentUser;
await messagesRef.add({
text: formValue,
createdAt: firebase.firestore.FieldValue.serverTimestamp(),
uid,
photoURL
})
setFormValue('');
}
return (<>
<form onSubmit={sendMessage}>
<input value={formValue} onChange={(e) => setFormValue(e.target.value)} placeholder="say something nice" />
<button type="submit" disabled={!formValue}>🕊️</button>
</form>
</>)
}
Chat Auto-scroll
In order to see the latest messages, the messages feed should auto-scroll to the bottom of the chat feed on each message. This can be handled when the user sends a message OR for every message with useEffect.
function ChatRoom() {
const dummy = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
dummy.current.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
}, [messages])
return (<>
<main>
{messages && messages.map(msg => <ChatMessage key={msg.id} message={msg} />)}
<span ref={dummy}></span>
</main>
</>)
}
Security
When creating a message, the following security rules ensure that a user…
- Is Signed in
- Is creating a document with a UID that matches their own.
- Is using less than 255 text characters.
- Is not trying to modify the timestamp.
- Is not banned.
Firestore Rules
rules_version = '2';
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
match /{document=**} {
allow read, write: if false;
}
match /messages/{docId} {
allow read: if request.auth.uid != null;
allow create: if canCreateMessage();
}
function canCreateMessage() {
let isSignedIn = request.auth.uid != null;
let isOwner = request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.uid;
let isNotLong = request.resource.data.text.size() < 255;
let isNow = request.time == request.resource.data.createdAt;
let isNotBanned = exists(
/databases/$(database)/documents/banned/$(request.auth.uid)
) == false;
return isSignedIn && isOwner && isNotLong && isNow && isNotBanned;
}
}
}
Banning Users
The rules above allow you to ban a user by setting their UID to as the document ID in the banned collection. This can be done automatically in a cloud function as shown in the video.
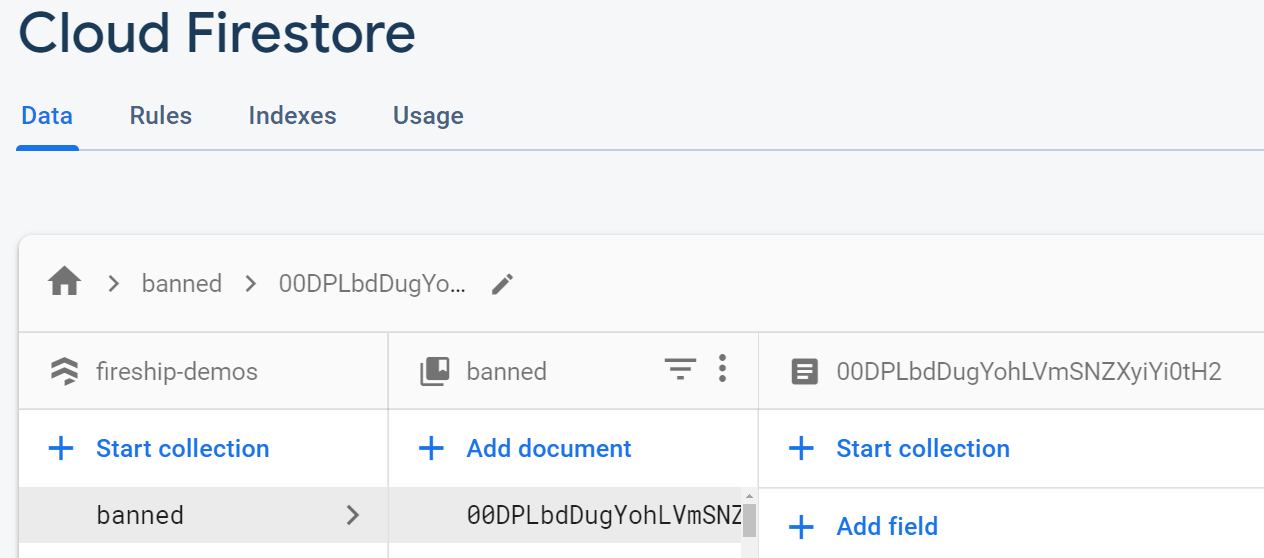
Example of banned document in Firestore. Does not require any fields.
